Fingerprint Scanners: What are the Different Types?
Are all fingerprint scanners the same? No, the methodology, quality and accuracy vary between different models and manufacturers. In this blog we examine the different types of fingerprint scanner and what you should look for if you are considering implement fingerprint access in your business.
Fingerprint scanner applications
The adoption of using fingerprints on smartphones to unlock screens by manufacturers has increased the acceptance of biometric recognition among consumers in everyday life. Biometric fingerprint scanners now play a role in access control for companies as well as being used in law enforcement and border control and payment systems.
There are many advantages of using fingerprints as a substitute for passwords and keys. Fingerprints are unique and can be forgery-proof when combined with the right technology. They cannot be lost, nor can they be lent, or left on the kitchen table in the morning.

Are fingerprint scanners all the same?
There are many other biometric authentication methods, but the fingerprint scanner is now the most widely used biometric identification method. It offers many advantages and is easy for companies to implement and use.
There are many different types of fingerprint scanners, from the way they work, their accuracy, security levels and cost. The following are the different types of fingerprint readers that are currently available on the market:
Optical fingerprint scanners
Optical fingerprint scanners are the most widely used type of reader. With this method, light-emitting diodes create a digital sample of the fingerprint. During the use of the access control terminal, the individual places their finger on the scan area.
An image of the fingerprint is then recorded and discarded, whilst the algorithm matches binary sequences against the stored binary template. This method is considered to be one of the most counterfeit-proof methods on the market.
Capacitive fingerprint scanner
The functionality of the capacitive sensors works similar to the optical sensors. However, the digital pattern is generated through electrical voltage. In contrast to the optical scanner, the user swipes their finger over the scanning surface.
This method also uses a comparison between the saved and the current pattern. Capacitive readers are less prone to forgery than their optical counterparts and are therefore more expensive. The system delivers excellent image quality and allows a small and compact installation.
Ultrasonic fingerprint scanner
Ultrasonic waves are emitted when the fingers are placed on the surface. These are thrown back by the finger and hit the sensor again. A specific pattern of the finger is created. This relatively new method enables the sensor to be attached under the display glass.
These types of sensors open new possibilities for device design because the touchscreen itself becomes a reader. The finger no longer has to be placed on a specific, limited point.
Thermal fingerprint scanner
With this method, sensors determine the minimum temperature differences between the finger lines and generate a thermal image of the finger placed on it. Thermal fingerprint readers have many disadvantages such as higher power consumption and performance that depend on the environment temperature.
Quality of images is key
The quality of an image generated by a fingerprint sensor is a fundamental and important parameter. High-quality images allow for a smaller sensor and a lower cost since more details are captured per area unit. The image quality depends on the sensors ability to detect weak signals and filter out undesired noise, without requiring too long and cumbersome exposure to the fingerprint. Ultrasonic and active capacitive sensors provide very high-quality images because they read the dermal skin layer, rather than the epidermal layer.
Accuracy of Different Types of Fingerprint Scanners
Different metrics can be used to rate the performance of a biometric factor, solution or application. The most common performance metrics are the False Acceptance Rate (FAR) and the False Rejection Rate (FRR). You should ask your supplier what these after for the solution you are considering.
FAR AND FRR
The False Acceptance rate (FAR) is the probability that the system incorrectly authorises a non-authorised person, due to incorrectly matching the biometric input with a template. The FAR is normally expressed as a percentage, which is the percentage of invalid inputs which are incorrectly accepted. So, for example, if there were 100 people enrolled and the FAR was 1% then 1 in 100 people would be incorrectly identified as authorised when using that reader.
The False Rejection Rate (FRR) is the probability that the system incorrectly rejects access to an authorised person, due to failing to match the biometric input with a template. The FRR is normally expressed as a percentage, following the FRR definition this is the percentage of valid inputs which are incorrectly rejected. A high level of these leads to poor user experience and frustration – they are authorised on the system, they place their finger on the reader, but it doesn’t work..
FAR and FRR figures quoted by manufacturers are as a result of tests conducted in ideal conditions.
In the real world, actual rates can also be influenced by the following factors:
- The quality of the biometric factor that is used
- The technical implementation of the biometric solution
- Good quality enrolment
- Environmental factors
FRR is strongly person dependent to the point at which a personal FRR can be determined for everyone. FRR might increase due to environmental conditions or incorrect use, for example when using dirty fingers on a fingerprint reader. Mostly FRR lowers when a user gains more experience in how to use the biometric device or software.
Which is more important?
FRR and FAR are both important when comparing different types and quality of fingerprint scanners but where you are using the fingerprint reader will dictate which metric is of more importance. For example, if a fingerprint scanner is used for physical access control into a research laboratory, the objective of the application is to disallow access to unauthorised individuals under all circumstances. It is clear that a very low FAR is needed for such an application, even if it comes at the price of a higher FRR.
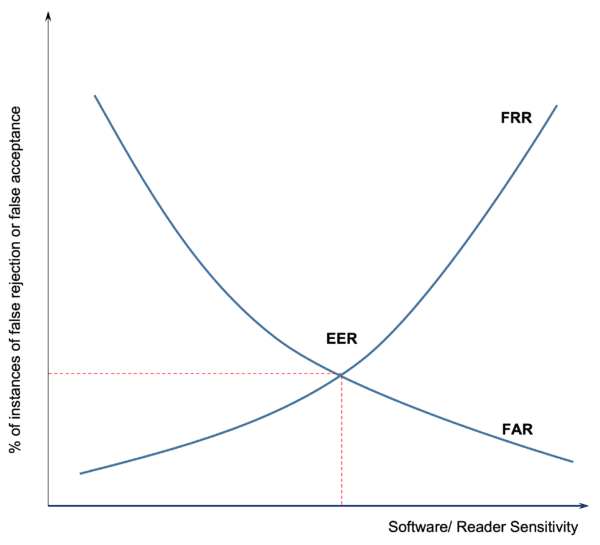
The two metrics generally have an inverse relationship. The point at which the two intersect is called the Equal Error Rate (EER). This is where the percentage of false acceptances and false rejections is the same.
If security is the most important factor on your site, then you can normally increase the sensitivity level in the accompanying access control software. This then means that the matching threshold is increased so the FAR will go down. It could also increase the risk of perfectly valid users being rejected if their fingers are dirty/ or wet or they don’t put their finger on the reader correctly. So it reduces user experience.
Conclusion:
There are many different types of fingerprint scanners on the market, and they are not all created equally. Capacitive and ultrasonic scanners are the most cost-efficient, flexible, secure and convenient technologies currently available on the market today, a good quality fingerprint scanner will accept authorised users and reject unauthorised ones, when they are installed and used properly.
Don’t Wait Until It’s Too Late: Secure Your Business’ Future Today with Almas Industries
The commercial landscape is in a state of constant flux, and so are the security challenges that come with it. There’s no time like the present to reassess and fortify your security measures.
Here are three reasons why you should reach out to us now.
1. Stay Ahead with Innovative Solutions: In a world where threats are becoming increasingly sophisticated, settling for outdated security systems is not an option. Our cutting-edge biometric and CCTV solutions ensure that you’re not just keeping up but staying ahead.
2. Tailored for You: Generic solutions often lead to vulnerabilities. We offer a bespoke approach to security, designed to meet the unique needs and challenges of your commercial business.
3. 24/7 Exceptional Customer Service: Security is a round-the-clock concern, and so is our customer service. From installation to regular maintenance checks, our support teams are always at your disposal to ensure seamless operation. Our installation and feedback scores from our customers in the last quarter were over 4.8/5.
Take the first step towards unparalleled commercial security by contacting Almas Industries. Secure your assets, safeguard your future—because your peace of mind is our business. Contact us today for more information on fingerprint scanners or any of our security solutions, 03335677799 (UK) or 016833368 (IRE) Or send us an email: [email protected]
More questions?
Here is our knowledge base about all things fingerprint scanners
Find out more information about our exceptionally stylish and high quality fingerprint scanners.




